1 mapreducer的配置
1.1 推测执行
Straggle(掉队者)是指那些跑的很慢但最终会成功完成的任务。一个掉队的Map任务会阻止Reduce任务开始执行。
Hadoop不能自动纠正掉队任务,但是可以识别那些跑的比较慢的任务,然后它会产生另一个等效的任务作为备份,并使用首先完成的那个任务的结果,此时另外一个任务则会被要求停止执行。这种技术称为推测执行(speculative execution)。
默认是开启推测执行
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.speculative</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>是否对Map Task启用推测执行机制</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.reduce.speculative</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>是否对Reduce Task启用推测执行机制</description>
</property> 有的时候要把 推测执行 关掉,这个一般是在代码中设置。
什么时候不合适开启推测执行呢?
如果你的输出是往MySQL数据库输出的,那么这个时候我们必须要关闭推测执行,因为推测执行是两个任务一起跑如果谁跑完了就kill掉对方,这样的话对我向数据库插入这种任务来说就会造成数据重复插入的问题,所以不能开启推测执行。
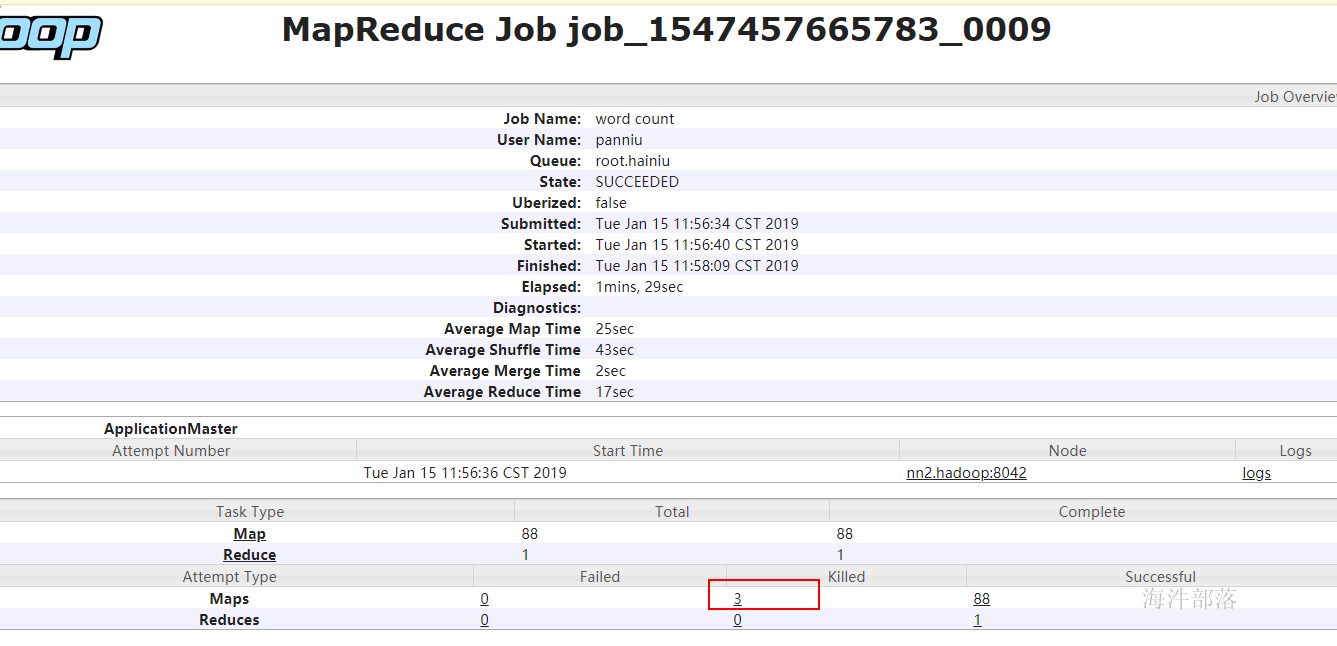
点击链接
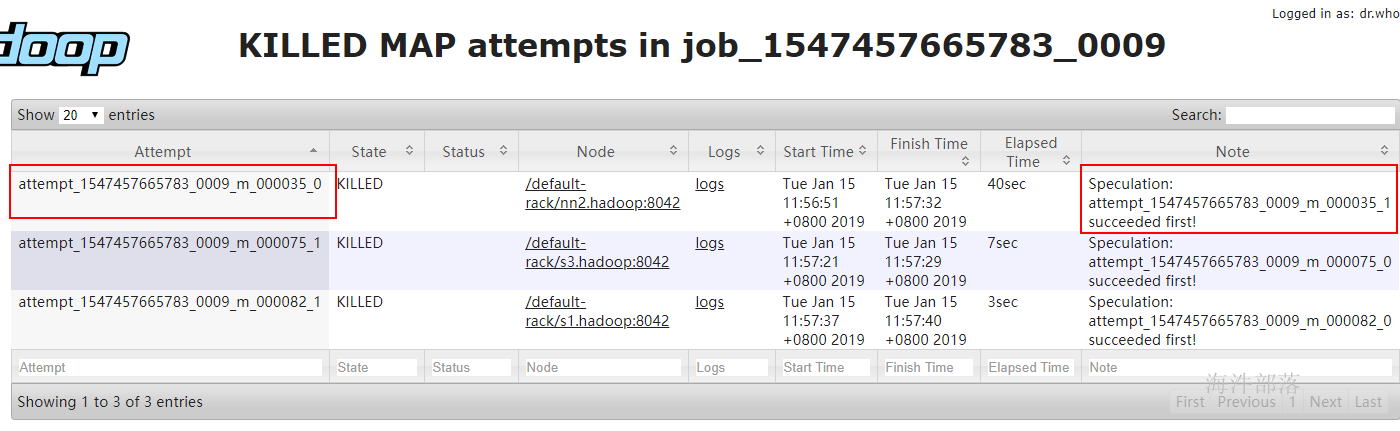
1.2 计数器
counters是mapreduce任务里的组件,用于统计。
在工作中需要统计那些不符合实际需求或规则的数据。在数据出现错误的时候,能快速定位到错误的原因。
系统的counters
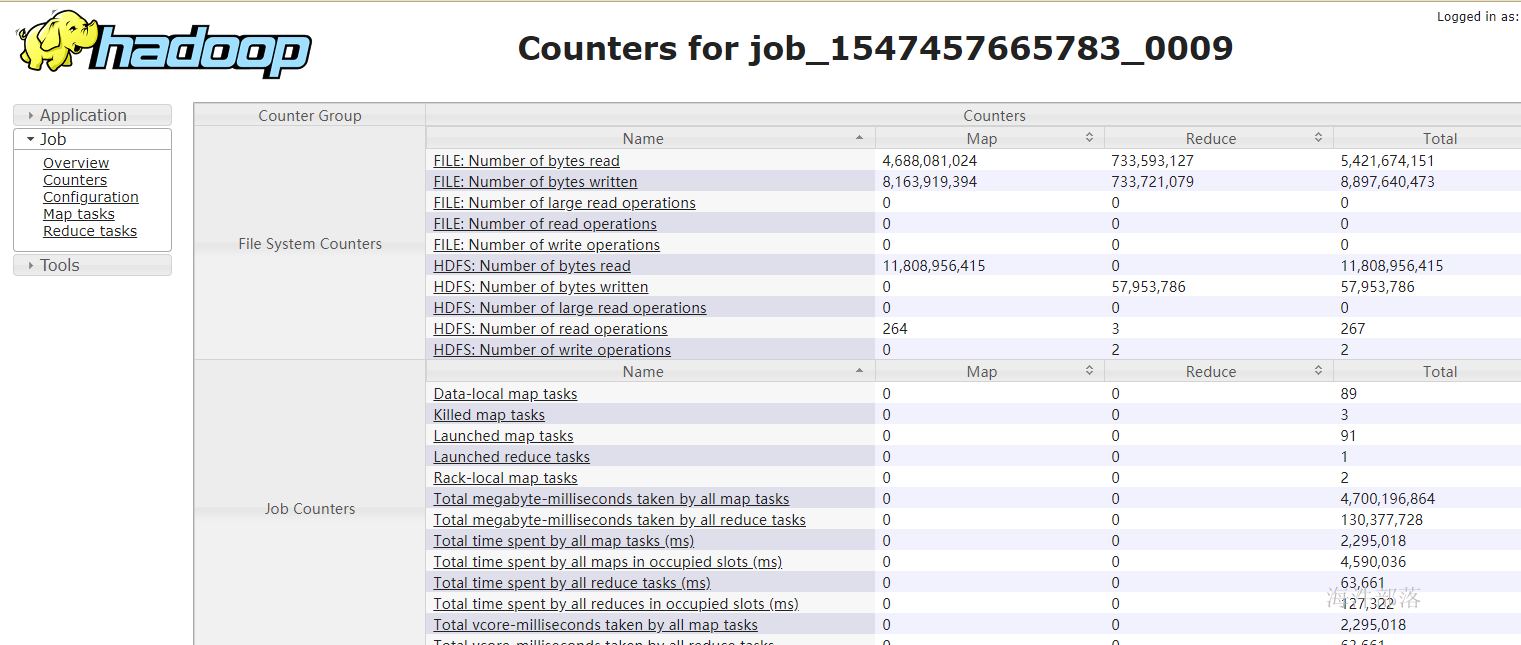
counter的默认是120
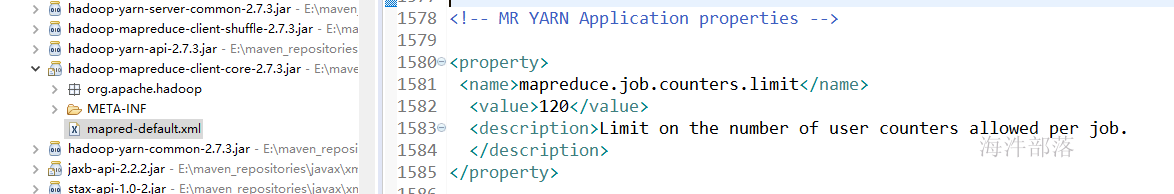
可以通过在mapred-site.xml里设置counter最大上限,counter的数量会影响appMaster的性能。

1)counter日志是如何打印的?
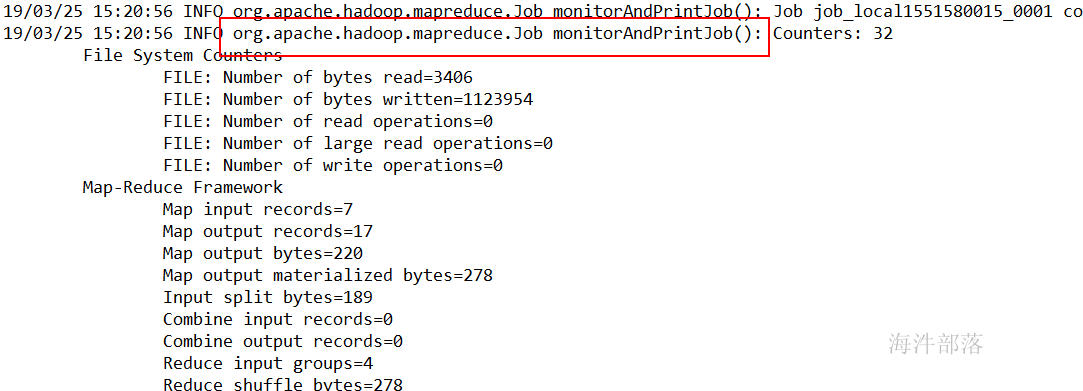
2)mapper里设置counter
统计一共有多少行 在mapper 中统计

3)reducer里设置counter
一共有多少种单词 在reducer中统计

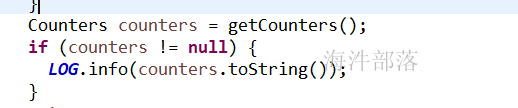
4)在任务完成之后取出想要使用的counter
// 提交job
boolean status = job.waitForCompletion(false);
// counter数据是在提交任务之后拿到的
Counters counters = job.getCounters();
// System.out.println(counters.toString());
// 获取hainiu组
CounterGroup group = counters.getGroup("hainiu");
//
System.out.println("==》遍历counter组");
for(Counter counter : group){
System.out.println("\t\t" + counter.getDisplayName() + "=" + counter.getValue());
}
// 查找counter组里的指定counter
System.out.println("==》查找counter组里的指定counter");
Counter findCounter = group.findCounter("line num");
System.out.println("写入到MySQL的数据是:" + findCounter.getDisplayName() + "=" + findCounter.getValue());
System.exit(status ? 0 : 1);
1.3 压缩设置
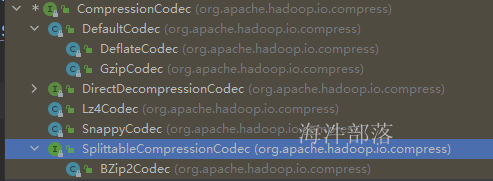
压缩类的结构树
1)设置reducer 压缩**输出**
第一种:用FileOutputFormat设置
// ---设置reduce输出压缩---
// 1)开启reduce输出压缩
FileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
// 2)设置输出压缩格式--gzip
FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class);
2)设置mapper 压缩**输出**
// ---设置map输出压缩---
// 方式1:
// // 开启map输出压缩
conf.set(MRJobConfig.MAP_OUTPUT_COMPRESS, "true");
// // 设置输出压缩格式是snappy压缩
conf.set(MRJobConfig.MAP_OUTPUT_COMPRESS_CODEC, SnappyCodec.class.getName());
// 创建运行mapreduce任务的Job对象
// 当创建job对象时,会把 conf里面的所有数据 拷贝到 job对象的Configuration里
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "wordcount");
// 方式2:
// 开启map输出压缩
job.getConfiguration().set(mapreduce.map.output.compress", "true");
// 设置输出压缩格式是snappy压缩
job.getConfiguration().set("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec", SnappyCodec.class.getName());如果运行报错例如:
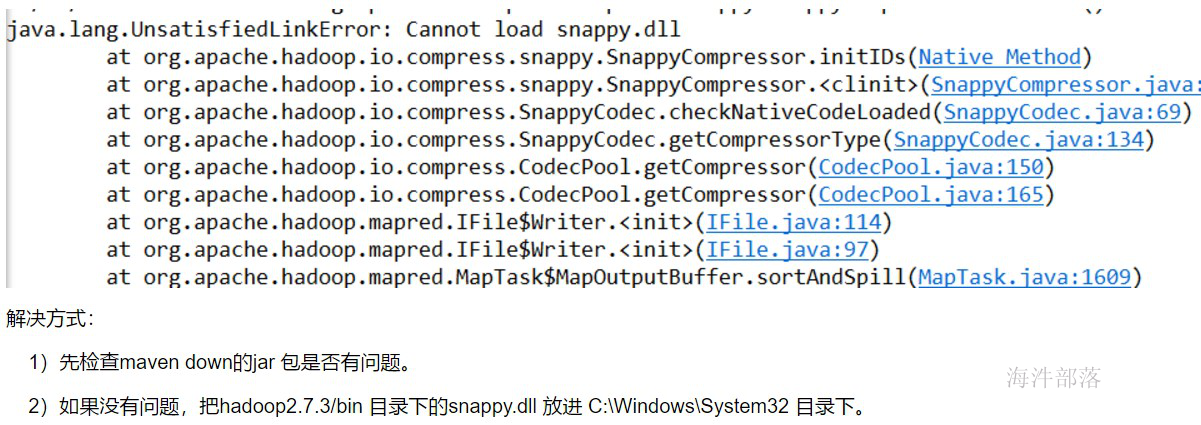
代码:
1.4 配置文件
<!-- 重要 start -->
<property>
<name>mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb</name>
<value>128</value>
<description>Map Task缓冲区所占内存大小</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.framework.name</name>
<value>yarn</value>
<description>运行模式</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.resource.mb</name>
<value>256</value>
<description>MR ApplicationMaster yarn申请的内存量</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.command-opts</name>
<value>-Xmx128m</value>
<description>jvm使用内存</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.resource.cpu-vcores</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>MR ApplicationMaster占用的虚拟CPU个数,此参数对应yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores,
建议最大为一个物理CPU的数量</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.speculative</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>是否对Map Task启用推测执行机制</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.reduce.speculative</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>是否对Reduce Task启用推测执行机制</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.memory.mb</name>
<value>512</value>
<description>每个Map Task yarn申请内存</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.reduce.memory.mb</name>
<value>512</value>
<description>每个Reduce Task yarn申请内存</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.reduce.java.opts</name>
<value>-Xmx410m</value>
<description>reduce jvm实际内存</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.java.opts</name>
<value>-Xmx410m</value>
<description>map jvm实际内存</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.cpu.vcores</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>每个map Task需要的虚拟cpu数</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.reduce.cpu.vcores</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>每个Reduce Task需要的虚拟cpu数</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.application.classpath</name>
<value>/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop,
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/*,
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/lib/*,
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/hdfs/*,
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/hdfs/lib/*,
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/*,
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/lib/*,
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/yarn/*,
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/yarn/lib/*,
/usr/local/hadoop/lib/*,
/usr/local/hbase/lib/*</value>
<description>运行mr程序所使用的虚拟机运行时的classpath</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.job.queuename</name>
<value>hainiu</value>
<description>提交mr任务时所使用的队列</description>
<!--<value>${hadoop.job.queuename}</value>-->
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.job.counters.limit</name>
<value>20000</value>
<description>mr允许使用的计数器的最大上限</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.output.compress</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>map是否开启输出压缩</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec</value>
<description>map输出默认的算法</description>
</property>
<!-- 重要 end -->
<!-- 目录相关 start -->
<property>
<name>mapreduce.local.dir</name>
<value>/data/mapred/data</value>
<description>linux本地目录</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.system.dir</name>
<value>/data/mapred/system</value>
<final>true</final>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.jobhistory.intermediate-done-dir</name>
<value>/data/mapred/tmp</value>
<description>MapReduce作业产生的日志存放位置</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.jobhistory.done-dir</name>
<value>/data/mapred/done</value>
<description>MR JobHistory Server管理的日志的存放位置</description>
</property>
<!-- 目录相关 end -->
<!-- 其它 -->
<property>
<name>mapreduce.task.io.sort.factor</name>
<value>20</value>
<description>溢出文件被合并成一个已分区切已排序的输出文件,控制一次最多能合并多少流</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.job.task.listener.thread-count</name>
<value>60</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.reduce.shuffle.parallelcopies</name>
<value>24</value>
<description>作为client端的reduce同时从map端拉取数据的并行度(一次同时从多少个map拉数据),
每个reduce并行下载map结果的最大线程数</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapred.reduce.copy.backoff</name>
<value>600</value>
<description>reduce下载线程最大等待时间(insec)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.tasktracker.http.threads</name>
<value>40</value>
<description>作为server端的map用于提供数据传输服务的线程数</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.jobhistory.address</name>
<value>nn1.hadoop:10020</value>
<description>MapReduce JobHistory Server地址</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.jobhistory.webapp.address</name>
<value>nn1.hadoop:19888</value>
<description>MapReduce JobHistory Server Web UI地址</description>
</property>2 mapreducer 优化
1)合理设置HDFS文件块的大小
块的大小和文件的数量决定了map任务的数量,根据服务器读取数据的速度进行数据块大小设置(hadoop2.7.3 128M)。
2)增加map buff缓冲区的大小
mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb 100 shuffle 的环形缓冲区大小,默认 100m
mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent 0.8 环形缓冲区溢出的阈值,默认 80%3)map输出的KEY的设计均匀
key设计不均衡的表现, reduce2执行完了,reduce1还在拉取数据,并且reduce2得等着reduce1完成,整个任务才算完成。
reduce1: 90w 个 a
reduce2: 10w 个 b
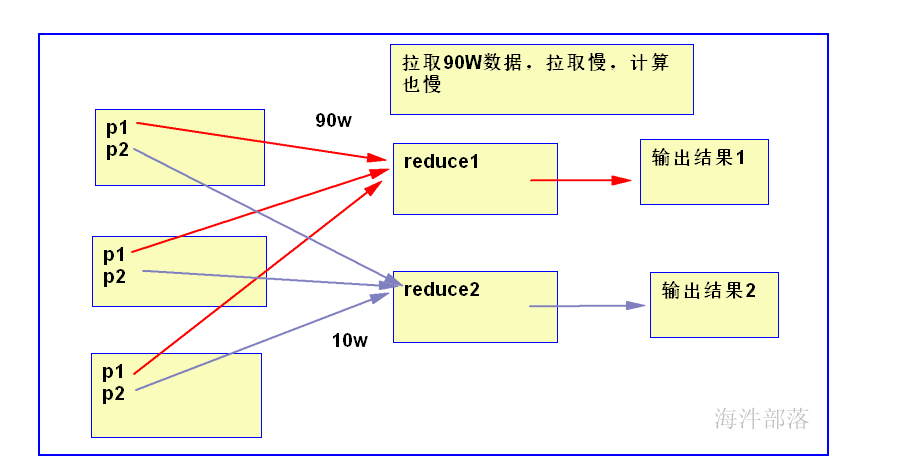
如何来解决key不均衡?
key: a ,90w 的 a key_随机数 或者 key_序列, 这样,不会将所有的90w个a拉取到一个reduce上。
之前:
90w a 如果key相同的话都会进入一个 reduce 中 所以这样会导致最终的reduce数据量过多而OOM
所以我们要想办法将key 重新设计
比如key 都是a 我们就可以采用后面加分隔符 加 随机数或者队列的方式进行操作
随机数
a_0.234345364356 --> 默认情况 parititoner --> hashpartitoner
a_0.344354354353
序列
a_0000000000000001
a_0000000000000002
a_0000000000000003
总结 : 由于key的重新设计 使我们以前分部在一起的数据 现在能够平均分部在多个文件里 虽然这样破坏了统计的key 但是做到了 化大为小的原则 假如你再想进行计算 可以在已经分好的数据中再次执行mapreduce
4)增加reduce的个数,通过分流加快reduce处理。
5)增加reduce copy buff缓冲区的大小,增加copy线程的线程数;
6)减少reduce阶段的数据输入量,在map阶段进行combiner 、map输出时进行数据压缩;
解决key不均衡问题代码:
/**
* WordCountKey.java
* com.hainiu.day01
* Copyright (c) 2021, 海牛版权所有.
* @author 薪牛
*/
package com.hainiu.day03;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Random;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
/**
* 实现Wordcount
* @author 薪牛
* @Date 2021年7月22日
*/
public class WordCountKey {
public static class WordCountKeyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable>{
/**
* 单词
*/
Text keyOut = new Text();
/**
* 数值
*/
LongWritable valueOut = new LongWritable();
Random random = new Random();
int seqNo = 1;
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("mapper input==>" + key.get() + ", " + value.toString());
// 获取一行的字符串
// one world
String line = value.toString();
// one, world
String[] arr = line.split(" ");
for(String word : arr){
// 分reduce数据的算法: hash(key) % reduceNum
// 通过修改key,使得数据能均衡些
// 方法1: 单词_随机数
// int randomNum = random.nextInt(10);
// keyOut.set(word + "_" + randomNum);
// 方法2:单词_序列
keyOut.set(word + "_" + seqNo++);
if(seqNo > 15){
seqNo = 1;
}
valueOut.set(1);
// 通过该方法输出数据 one,1
context.write(keyOut, valueOut);
System.out.println("mapper output==>" + keyOut.toString() + ", " + valueOut.get());
}
}
@Override
protected void cleanup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("==>cleanup()");
}
}
public static class WordCountKeyReducer extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable>{
Text keyOut = new Text();
LongWritable valueOut = new LongWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// one, [1,1,1,1] ---> one,4
long sum = 0L;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("reducer input==>");
sb.append(key).append(", [");
for(LongWritable w : values){
sb.append(w.get()).append(",");
sum += w.get();
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1).append("]");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
valueOut.set(sum);
String word = key.toString().split("_")[0];
keyOut.set(word);
context.write(keyOut, valueOut);
System.out.println("reducer output==>" + keyOut + ", " + sum);
}
}
// /tmp/mr/input /tmp/mr/output
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 加载 core-default.xml 和 core-site.xml
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 创建运行mapreduce任务的Job对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "wordcount");
// 设置运行的类(linux 运行用)
job.setJarByClass(WordCountKey.class);
// 设置mapperclass
job.setMapperClass(WordCountKeyMapper.class);
// 设置reducerclass
job.setReducerClass(WordCountKeyReducer.class);
// 设置reducer个数, 不设置默认是1
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
// 设置mapper输出keyclass
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// 设置mapper输出valueclass
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
// 设置reducer输出keyclass
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// 设置reducer输出的valueclass
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
// 设置读取的输入文件的inputformatclass,默认是文本,可以不设置
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
// 设置写入文件的outputformatclass,默认是文本,可以不设置
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
// 设置输入目录
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
Path outputPath = new Path(args[1]);
// 设置输出目录
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 自动删除输出目录
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
// 如果输出目录存在,就递归删除输出目录
if(fs.exists(outputPath)){
// 递归删除输出目录
fs.delete(outputPath, true);
System.out.println("delete outputPath==> 【" + outputPath.toString() + "】 success!");
}
// 提交job
boolean status = job.waitForCompletion(false);
System.exit(status ? 0 : 1);
}
}运行参数:
/tmp/mr/input_keys /tmp/mr/output
查看日志发行reduce接收的数据相对均衡
reduce1:

reduce2:

3 combiner的使用
combiner的本质是reducer, 利用reducer进行聚合得到局部聚合结果。
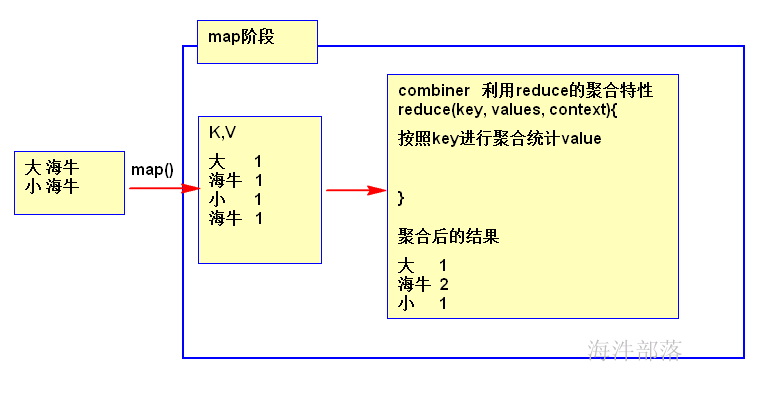
/**
* WordCount3.java
* com.hainiu
* Copyright (c) 2021, 海牛学院版权所有.
*/
package com.hainiu;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Counter;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.CounterGroup;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Counters;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.Context;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.LineRecordReader;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
/**
* 带有combiner的wordcount
* combiner 本质上是mapper端有个reducer
* 步骤:
* 1) 定义combiner 的reducer, 实现mapper内部的局部聚合
* 2)在job中设置combinerclass
* @author 薪牛
* @Date 2021年3月8日
*/
public class WordCount3 {
public static class WordCount3Mapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable>{
/**
* 输出key:单词
*/
Text keyOut = new Text();
/**
* 输出value:1
*/
LongWritable valueOut = new LongWritable(1);
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// map() 一行调用一次
// one world --> one 1
// world 1
String line = value.toString();
String[] arr = line.split(" ");
for(String word : arr){
keyOut.set(word);
// 输出k,v
context.write(keyOut, valueOut);
// System.out.println("mapper output==> " + word + ", " + valueOut.get());
}
}
}
/*
* combiner 的reducer 输入和输出,要与mapper输出的类型一致
*/
public static class WordCount3Reducer2 extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable>{
LongWritable valueOut = new LongWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("mapper reduce input==> " + key + ", [");
long sum = 0L;
for(LongWritable w : values){
long n = w.get();
sb.append(n).append(",");
sum += n;
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
sb.append("]");
System.out.println(sb);
valueOut.set(sum);
context.write(key, valueOut);
System.out.println("mapper reduce output==>" + key + ", " + sum);
}
}
public static class WordCount3Reducer extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable>{
LongWritable valueOut = new LongWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("reduce input==> " + key + ", [");
long sum = 0L;
for(LongWritable w : values){
long n = w.get();
sb.append(n).append(",");
sum += n;
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
sb.append("]");
System.out.println(sb);
valueOut.set(sum);
context.write(key, valueOut);
System.out.println("reducer output==>" + key + ", " + sum);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建Hadoop的configuration对象, 加载公共配置
// addDefaultResource("core-default.xml");
// addDefaultResource("core-site.xml");
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 创建MapReduce的job对象,此时加载运行MapReduce相关的配置
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "wordcount");
// 集群运行是找class用的
job.setJarByClass(WordCount3.class);
// 设置运行的mapper类
job.setMapperClass(WordCount3Mapper.class);
// 设置运行的reducer类型
job.setReducerClass(WordCount3Reducer.class);
// 默认是1,设置reducer个数
job.setNumReduceTasks(1);
// 【设置combinerclass】
job.setCombinerClass(WordCount3Reducer2.class);
// 设置mapper类keyOutclass
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// 设置mapper类valueoutclass
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
// 设置最终keyOutclass
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// 设置最终valueOutclass
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
// 设置读取输入文件的inputformatclass, 当处理的是普通文本时,下面两个都是默认,不设置也可以
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
// 设置写入文件的outputformatclass
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
// 设置输入目录
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
Path outputPath = new Path(args[1]);
// 增加自动删除输出目录
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
if(fs.exists(outputPath)){
// 递归删除
fs.delete(outputPath, true);
System.out.println("delete outputpath==>【 " + outputPath.toString() + " 】 success!");
}
// 设置输出目录
// 如果输出目录存在就报错
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 提交job
// true:打印counter, false:不打印
job.waitForCompletion(false);
}
}运行参数:
/tmp/mr/input_keys /tmp/mr/output
不加combiner\日志**:**
reducer 输入和输出

**
加combiner 日志:
combiner输入和输出

reducer 输入和输出

源码分析combiner运行过程:
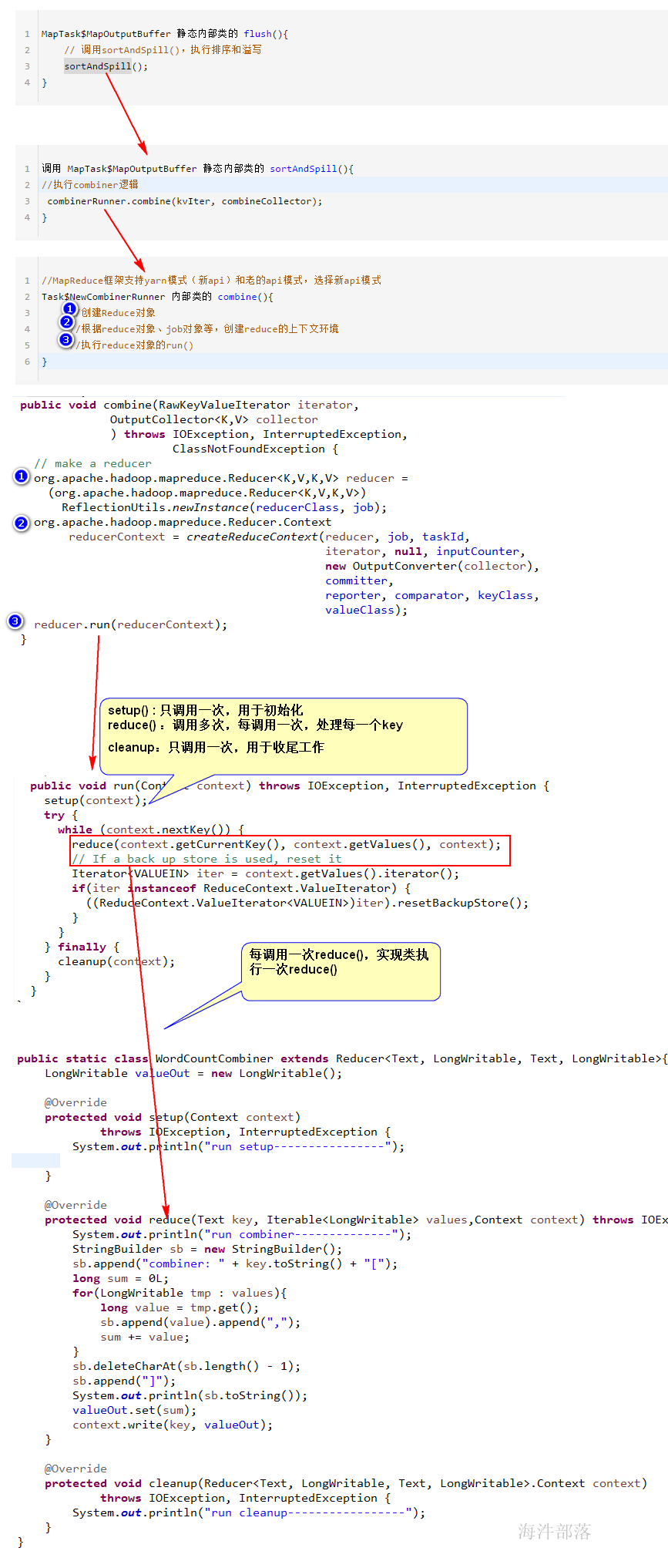
4 如何设置 reducer 个数
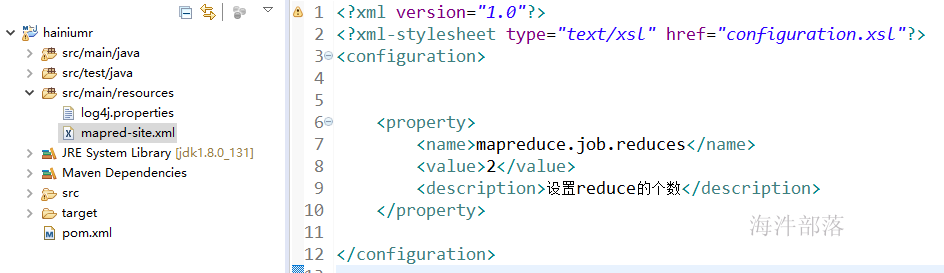
reducer的个数决定最终输出文件的个数,可以通过以下方式设定
1)job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
2)conf.set()
3)通过在mapred-site.xml 配置参数
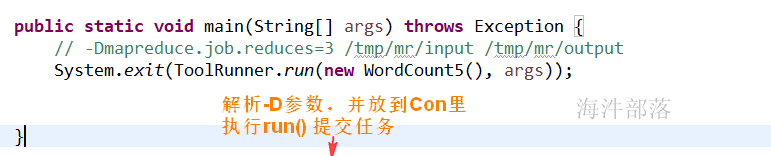
4)通过 -Dmapreduce.job.reduces 参数设定
执行任务运行参数加入-D参数,通过这样方式实现个性化配置
多个-D参数设置: -Dkey=value -Dkey2=value2 -Dkey3=value3
-D 参数要放在输入输出目录前面
运行参数:-Dmapreduce.job.reduces=2 /tmp/mr/input /tmp/mr/output
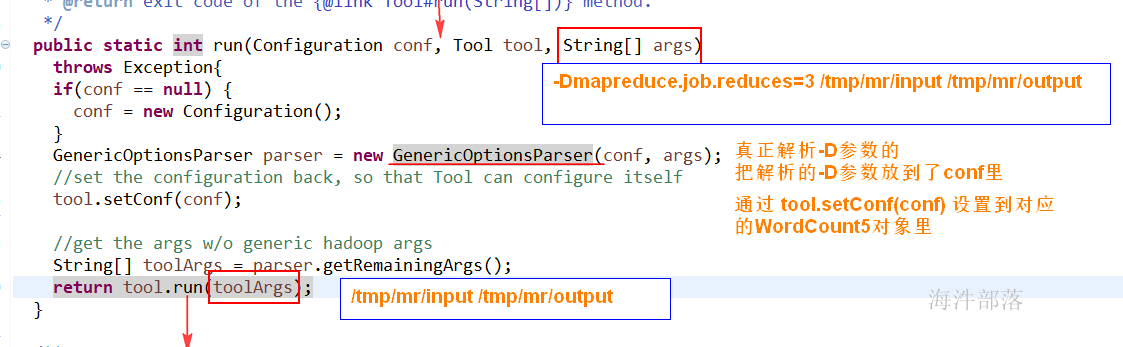
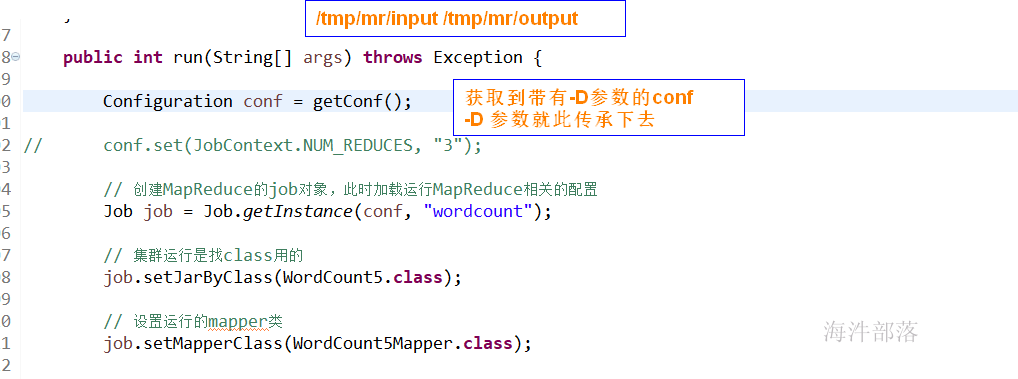
5 配置参数的四种方式总结
5.1 四种方式
1)job api 设置
此种方式是程序员优先使用的方式。如设置job相关的配置。
2)conf.set()****
此种方式是job 的api 设置不了配置时,才使用的方式。如开启 map压缩输出。
3)mapred-site.xml
开发环境中放到项目里的resource目录就可以生效,因为这个目录是配置到项目的Build Path里的,为什么加载这个文件是由hadoop的configuration的配置文件加载机制决定的。
linux环境(正式环境)maprd-site.xml是放到/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop目录下的。
xml配置文件方式不灵活,适合这种一经确定就不需要改变的配置。
4)-D参数
-Dname=value 用来给配置参数传值;
-D 要放在其他参数的前面,如 -Duser.name=hainiu /tmp/input/word.txt /tmp/output
-D参数适合个性化配置。
-D参数是如何进入到job对象的configuration对象的?
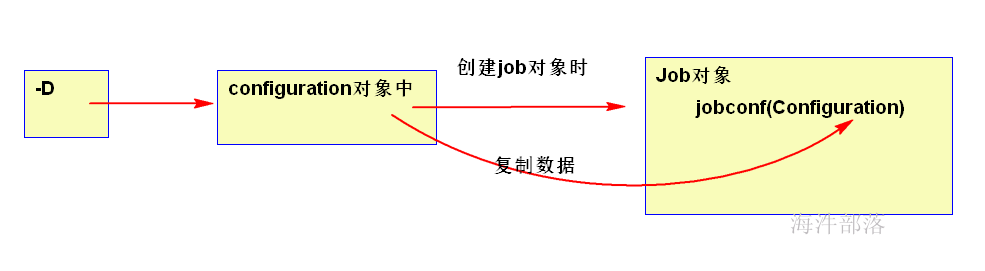
5.2 如果四种方式配置冲突了,哪个配置会生效?
如果-D参数和mapred-site.xml 冲突了,-D参数会生效。
如果-D参数和conf.set() 或 job api 设置冲突了, 后两者会生效。
如果conf.set() 和 job api 设置冲突了,哪个后设置,哪个会生效。
记住结论。
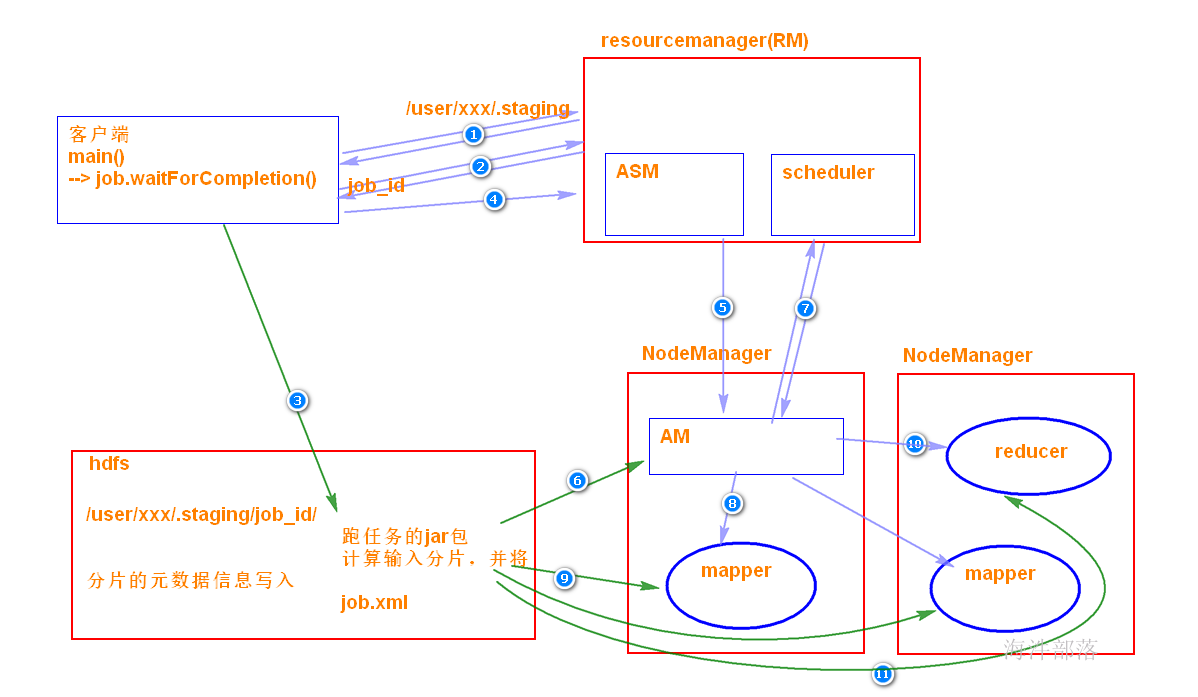
6 Job提交的任务流程
6.1 waitForCompletion
在mapreduce程序的job类中,我们通过set Configuration对象,得到相应的job对象,在job对象中指定Mapper类、Reducer类,Job类等属性后,通过waitForCompletion(true)方法提交并等待job执行。传入的boolean类型参数决定是否监控并打印job的执行情况。
方法首先检查Job状态,若处于DEFINE状态则通过submit()方法提交job。而后根据传入的参数决定是否监控并打印job的运行状况。
6.2 submitJobInternal
在 Job 对象上面调用 submit() 方法之后,在内部创建一个 JobSubmitter 实例,然后调用该实例的 submitJobInternal() 方法。
任务提交器(JobSubmitter)是最终提交任务到集群的方法。
执行过程如下:
1)首先checkSpecs(job) 检查作业输出路径是否配置并且是否存在,如果存在抛异常。
2)请求资源管理器,通过JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir()获取作业执行时相关资源的存放路径。
3)请求资源管理器,获取运行job的jobId,并将jobId设置进job对象中,构造提交job的路径。然后是对该路径设置一系列权限的操作。
4)copyAndConfigureFiles,拷贝作业运行必备的资源,作业 JAR 文件。
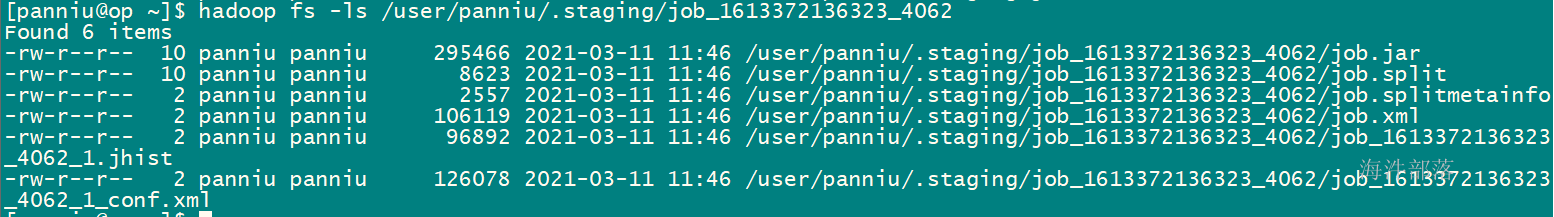
5)调用writeSplits()方法,(非常重要)为作业计算输入分片(input splits)。写分片数据文件job.splits和分片元数据文件job.splitmetainfo,计算map任务数。
6)writeConf()方法,写 job.xml 配置文件
7)提交作业submitClient.submitJob,通过在资源管理器上调用 submitApplication 来提交作业。
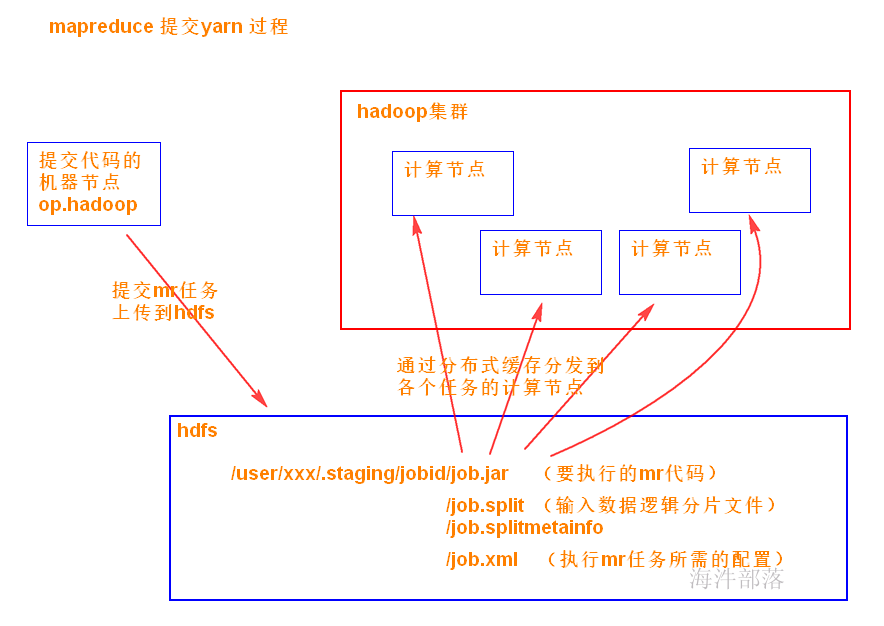
集群运行后killI掉查看:
重点:
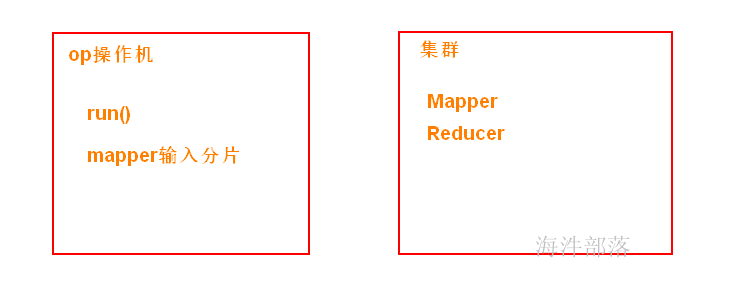
mapreduce 如果在windows本地运行:
那 运行Mapper阶段和Reducer阶段都是线程。
比如:job 运行两个Mapper,两个Reducer,那就是4个线程,相当于1个jvm开启4个线程。
mapreduce 如果在分布式集群运行:
那 运行Mapper阶段和Reducer阶段都是进程。
比如:job 运行两个Mapper,两个Reducer,那就是4个进程,相当于开启4个jvm。
7 innerjoin

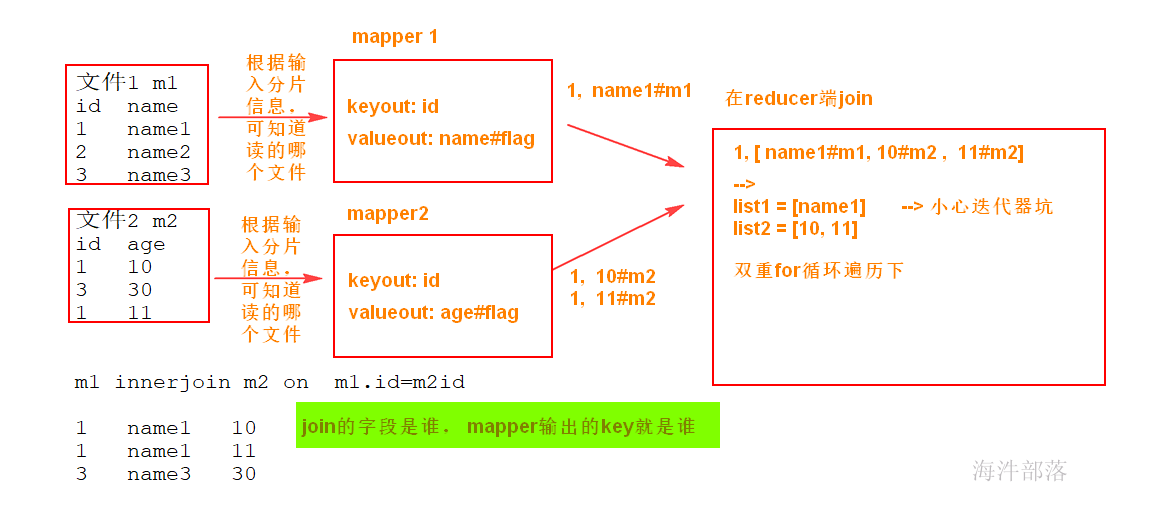
1)在mapreduce的哪个阶段进行join?
reduce
2)reduce阶段join的时候,你按照什么进行join,怎么知道哪个是map1的数据和哪个是map2数据进行join?
在map阶段输出的时候,来设定。
key: 你按照什么join,key就是啥
value: 你要join在一起的数据, 并且需要标记出是哪个map的数据。
/**
* order表
* id user goods num address
* 1 zhangsan 001 8 beijing
* 2 lisi 002 3 hangzhou
*
* goods
* id name price
* 001,iphone13 9999
* 002,xiaomi 1999
*/
public class JoinMR {
public static class JMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String k = null;
if(value.toString().indexOf(",") >-1) {
//goods文件
k = value.toString().split(",")[0];
}else
k = value.toString().split(" ")[2];
context.write(new Text(k), value);
}
}
public static class JReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable>{
@Override
protected void reduce(Text arg0, Iterable<Text> arg1, Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context arg2)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String orderInfos = null;
String goodsInfo = null;
for(Text t:arg1) {
if(t.toString().indexOf(",") > -1)
goodsInfo = t.toString();
else
orderInfos =t.toString();
}
//处理数据
String[] gsplit = goodsInfo.split("[,| ]");
String[] osplit = orderInfo.split(" ");
String allStr = osplit[0]+" "+osplit[1]+" "+gsplit[1]+" "+gsplit[2]+" "+osplit[3]+" "+osplit[4];
arg2.write(new Text(allStr), NullWritable.get());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Path in = new Path("join");
Path out = new Path("joinRes");
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.getLocal(conf);
if(fs.exists(out))
fs.delete(out);
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(JoinMR.class);
job.setMapperClass(JMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, in);
// job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
job.setReducerClass(JReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, out);
boolean success = job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}如果两个文件格式不一样,长度一样怎么判断呢?
/**
*user.txt
1 zhangsan 001
2 lisi 002
3 wangwu 003
4 zhaosi 004
5 liuneng 005
6 guangkun 006
*
*score
001 math 100
002 math 98
003 math 94
004 math 95
005 math 90
006 math 85
*reduce
*001 ["u_1 zhangsan 001","s_001 math 90"]
*/
public class JoinMr2 {
public static class JMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{
String filename = null;
String prefix = null;
@Override
protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取的切片信息不是切片数据的整体,只是知道了处理的文件是哪个
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit();
Path path = inputSplit.getPath();
filename = path.getName();
if(filename.contains("user"))
prefix = "u_";
else
prefix = "s_";
System.out.println(filename+"*************************");
}
Text k = new Text();
Text v = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//根据文件的名称就知道处理逻辑了
if(filename.contains("user")) {
k.set(value.toString().split(" ")[2]);
}else
k.set(value.toString().split(" ")[0]);
v.set(prefix+value.toString());
context.write(k,v);
}
}
public static class JReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable>{
@Override
protected void reduce(Text arg0, Iterable<Text> arg1, Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context arg2)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 001 ["u_1 zhangsan 001","s_001 math 90"]
String userInfo = null;
String scoreInfo = null;
for(Text t:arg1) {
if(t.toString().startsWith("u_"))
userInfo = t.toString();
else
scoreInfo = t.toString();
}
String[] usplit = userInfo.split("[_| ]");
String[] ssplit = scoreInfo.split("[_| ]");
String allStr = usplit[1]+" "+usplit[2]+" "+ssplit[2]+" "+ssplit[3];
arg2.write(new Text(allStr), NullWritable.get());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Path in = new Path("join1");
Path out = new Path("joinres");
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.getLocal(conf);
if(fs.exists(out))
fs.delete(out);
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(JoinMr2.class);
job.setMapperClass(JMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, in);
job.setReducerClass(JReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, out);
boolean success = job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}


