1 HIVE SELECT 语法
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ...
FROM table_reference
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY col_list]
[ORDER BY col_list]
[CLUSTER BY col_list | [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] [SORT BY col_list] ]
[LIMIT number]基于MapReduce引擎
Map阶段:
1.执行from加载,进行表的查找与加载
2.执行where过滤,进行条件过滤与筛选
3.执行select查询:进行输出项的筛选
4.执行group by分组:描述了分组后需要计算的函数
5.map端文件合并:map端本地溢出写文件的合并操作,每个map最终形成一个临时文件。
然后按列映射到对应的Reduce阶段:
Reduce阶段:
1.group by:对map端发送过来的数据进行分组并进行计算。
2.select:最后过滤列用于输出结果
3.limit排序后进行结果输出到HDFS文件注意,以上顺序不是绝对的,会根据语句的不同,有所调整。
可以通过执行计划查看大概顺序。
explain sql语句map端第一个操作肯定是加载表,所以就是 TableScan 表扫描操作,常见的属性:
alias: 表名称
Statistics: 表统计信息,包含表中数据条数,数据大小等
Select Operator: 选取操作,常见的属性 :
expressions:需要的字段名称及字段类型
outputColumnNames:输出的列名称
Statistics:表统计信息,包含表中数据条数,数据大小等
Group By Operator:分组聚合操作,常见的属性:
aggregations:显示聚合函数信息
mode:聚合模式,值有 hash:随机聚合,就是hash partition;partial:局部聚合;final:最终聚合
keys:分组的字段,如果没有分组,则没有此字段
outputColumnNames:聚合之后输出列名
Statistics: 表统计信息,包含分组聚合之后的数据条数,数据大小等
Reduce Output Operator:输出到reduce操作,常见属性:
sort order:值为空 不排序;值为 + 正序排序,值为 - 倒序排序;值为 +- 排序的列为两列,第一列为正序,第二列为倒序
Filter Operator:过滤操作,常见的属性:
predicate:过滤条件,如sql语句中的where id>=2,则此处显示(id >= 2)
Map Join Operator:join 操作,常见的属性:
condition map:join方式 ,如Inner Join 0 to 1
keys: join 的条件字段
outputColumnNames: join 完成之后输出的字段
Statistics: join 完成之后生成的数据条数,大小等
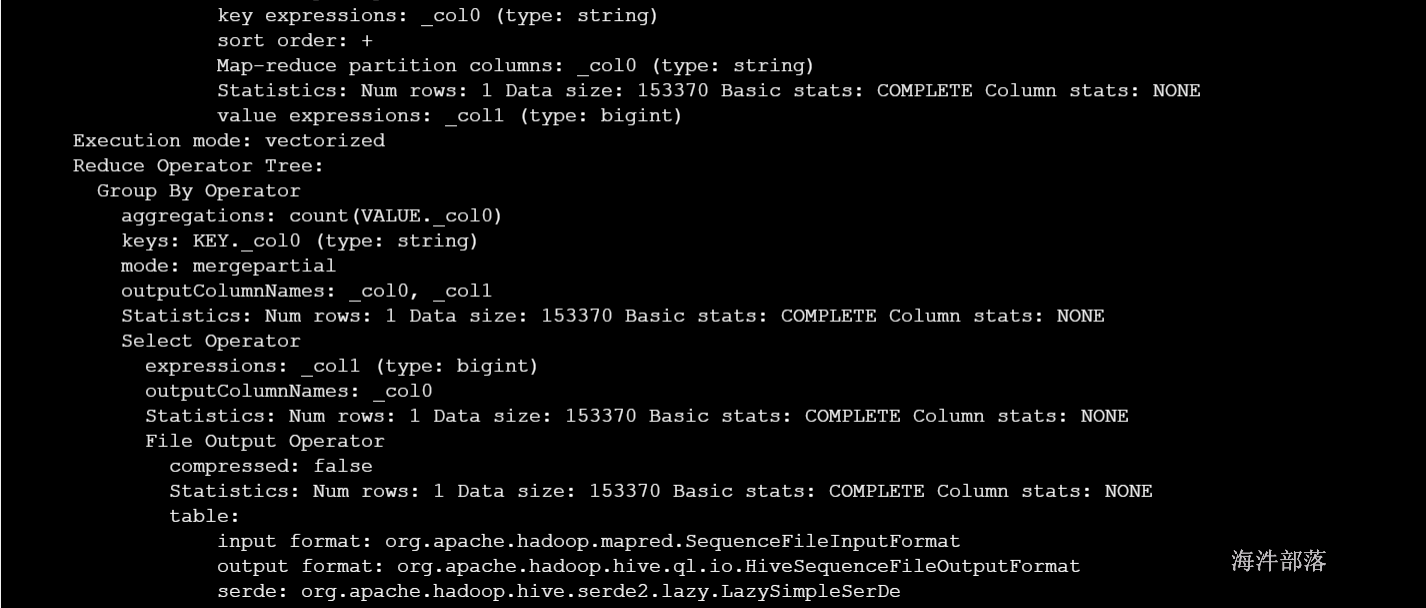
File Output Operator:文件输出操作,常见的属性
compressed:是否压缩
table:表的信息,包含输入输出文件格式化方式,序列化方式等
Fetch Operator 客户端获取数据操作,常见的属性:
limit,值为 -1 表示不限制条数,其他值为限制的条数
explain select count(*) from user_install_status_limit group by country;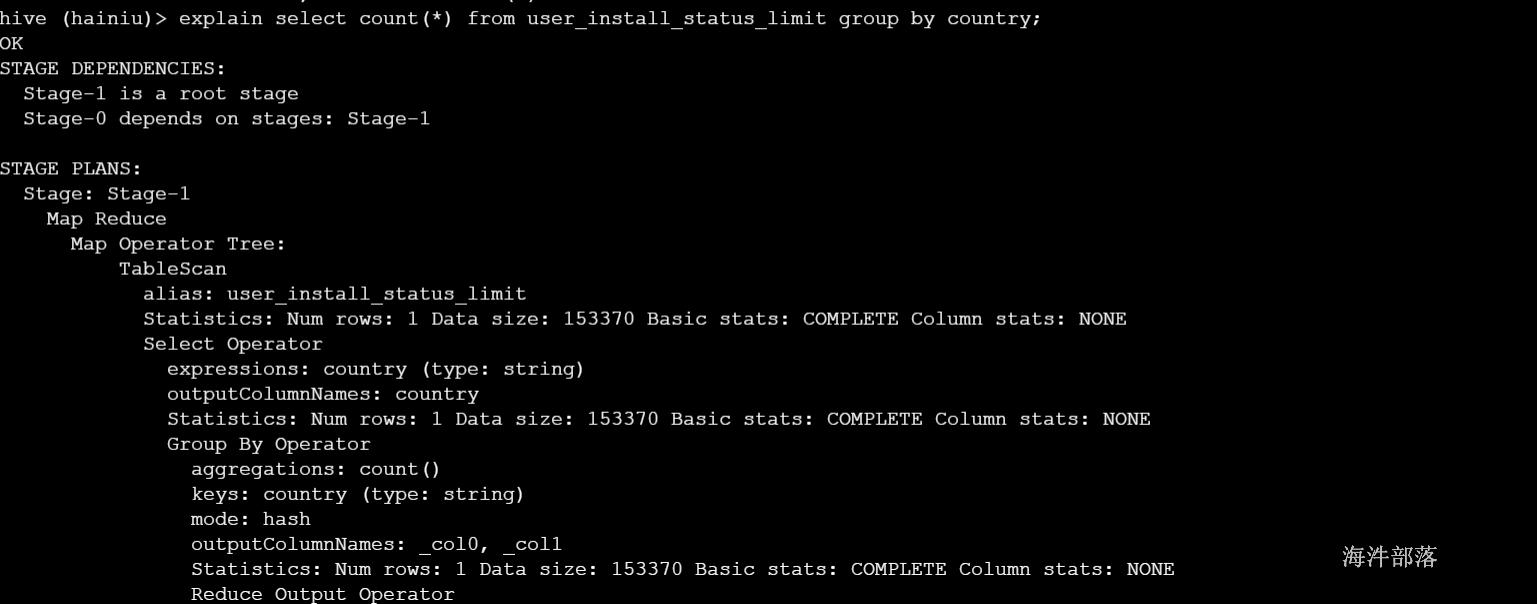

2 Hive Join
hive只支持等连接,外连接。hive不支持非相等的join条件(通过其他方式实现,如left outer join),因为它很难在map/reduce job实现这样的条件。
hive可以join两个以上的表。
如果两个以上join,join的字段都一样,类型也一样,那就只生成一个mapreduce任务。
2.1 两表join
建表导入数据
-- 创建表test_a
CREATE TABLE test_a(
id int,
name string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t';
-- 创建表test_b
CREATE TABLE test_b(
id int,
name string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t';
--创建表test_c
CREATE TABLE test_c(
id int,
name string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t';
--分别导入数据到三个表中
--test_a
1 a1
2 a2
4 a4
--test_b
1 b1
3 b3
4 b4
--test_c
1 c1
4 c4
5 c52.1.1 等值连接:inner join
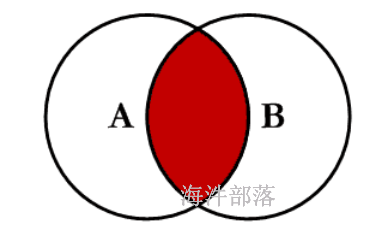
-- 关闭mapjon
set hive.auto.convert.join=false;
set hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint=false;
select * from test_a a inner join test_b b on a.id=b.id;
1 a1 1 b1
4 a4 4 b42.1.2 外连接:left join 、right join
普通left Join
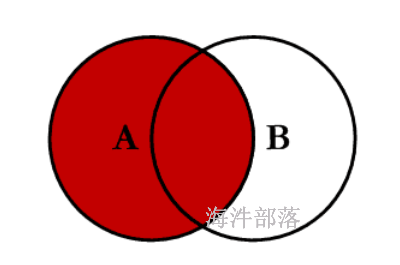
set hive.auto.convert.join=false;
set hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint=false;
select * from
test_a a left join test_b b on a.id=b.id;
1 a1 1 b1
2 a2 null null
4 a4 4 b4普通right Join
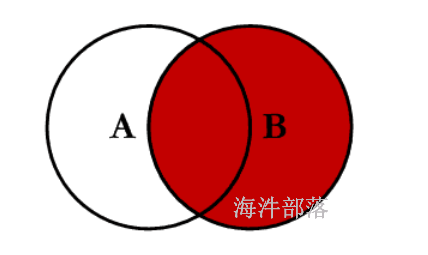
--right join
set hive.auto.convert.join=false;
set hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint=false;
select a.*,b.* from test_a a
right join test_b b
on a.id=b.id;
1 a1 1 b1
null null 3 b3
4 a4 4 b42.1.3 实现非等值连接
查询test_a有,test_b没有,用 left join + is null
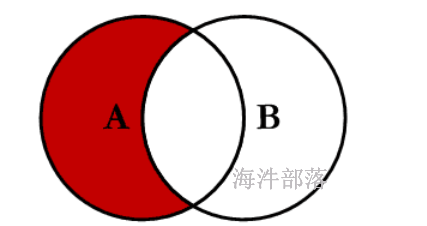
查询test_a没有,test_b有,用 right join + is null
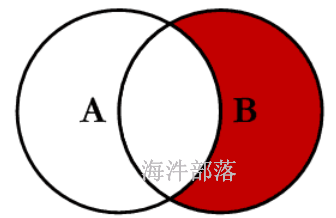
--在得到join结果后,再根据where条件筛选
set hive.auto.convert.join=false;
set hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint=false;
select a.*,b.* from test_a a
left join test_b b
on a.id=b.id
where b.id is null;
2 a2 null null
-- 错误例子
select a.*,b.* from test_a a
left join test_b b
on a.id=b.id and b.id is null;
1 a1 NULL NULL
2 a2 NULL NULL
4 a4 NULL NULL2.2 多表join
1)三表inner join
如果join的字段相同,只生成一个任务
测试:
先关闭map端的join,再执行
测试join字段相同,只生成一个任务
-- 关闭mapjon
set hive.auto.convert.join=false;
set hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint=false;
select * from test_a a
inner join test_b b on a.id=b.id
inner join test_c c on a.id=c.id;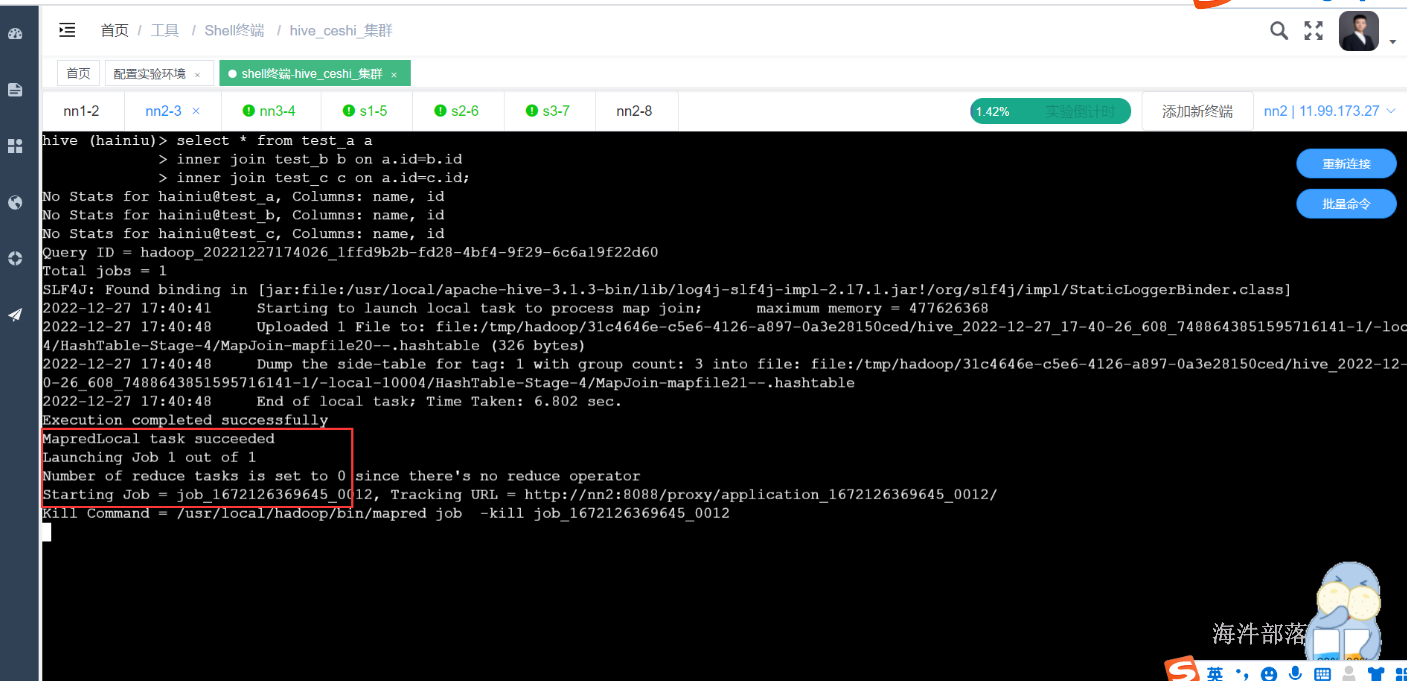
-------------------------------------
join字段不同,不一定生成一个任务
-- 关闭mapjon
set hive.auto.convert.join=false;
set hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint=false;
select * from test_a a
inner join test_b b on a.id=b.id
inner join test_c c on a.name=c.name; select * from test_a a
inner join test_b b on a.id=b.id
inner join test_c c on a.name=c.name;
2)计算新增用户(非等值连接的应用)
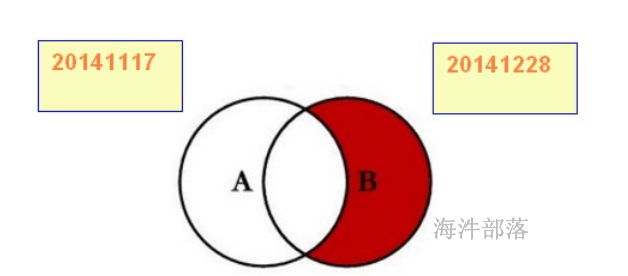
CREATE TABLE user_ttt(
aid STRING
)
PARTITIONED BY (dt STRING)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t';
alter table user_ttt add IF NOT EXISTS partition(dt='20141117') location '20141117';
alter table user_ttt add IF NOT EXISTS partition(dt='20141218') location '20141218';
select aid from user_ttt where dt='20141117' group by aid
aid1
aid2
aid3
select aid from user_ttt where dt='20141218' group by aid
aid1
aid2
aid4
aid5
select count(*) from
(select aid from user_ttt where dt='20141117' group by aid) t1
right join
(select aid from user_ttt where dt='20141218' group by aid) t2
on t1.aid = t2.aid where t1.aid is null;
aid1 aid1
aid2 aid2
null aid4
null aid53)计算每个国家记录数的百分比
-- 统计所有记录数
select count(*) from user_install_status_limit;
100
-- 统计每个国家的记录数
select country, count(*) from user_install_status_limit group by country;
CN 50
US 20
RU 30
CN 100 50 50%
US 100 20 20%
RU 100 30 30%
-- 统计每个国家占总记录数的占比
select t1.total_num, t2.country, t2.num, concat(round(t2.num/t1.total_num * 100, 2),'%') from
(select count(*) as total_num, 'link' as link from user_install_status_limit) t1
inner join
(select country, count(*) as num, 'link' as link from user_install_status_limit group by country) t2
on t1.link=t2.link;
hive (hainiu)> select concat("aa","bb");--round,默认取整,如果想精确,那就在后面加精确几位小数
--四舍五入取整
select round(5/3);
--精确6位小数
select round(5/3,6);
2.3 要避免的查询操作
--笛卡尔积的SQL
select * from test_a
inner join test_b;set hive.mapred.mode=strict;设置这个参数,可以限制以下情况:
1)限制执行可能形成笛卡尔积的SQL;
2)partition表使用时不加分区;
3)order by全局排序的时候不加limit的情况;
partition表使用时不加分区
order by全局排序的时候不加limit的情况

取消限制
set hive.mapred.mode=nonstrict;
2.4 full outer join
包括两个表的join结果,(左边有,右边NULL union 右边有,左边NULL)
其结果等于left join union right join
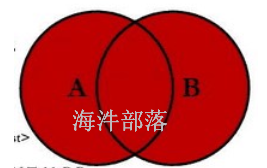
1)做test_a 与 test_b 的full outer join
select a.*,b.* from test_a a
full outer join
test_b b
on a.id=b.id;2.5 union的使用
union 是把两个表连接在一起,然后去重。
用 left join union right join 实现 full outer join
比如:
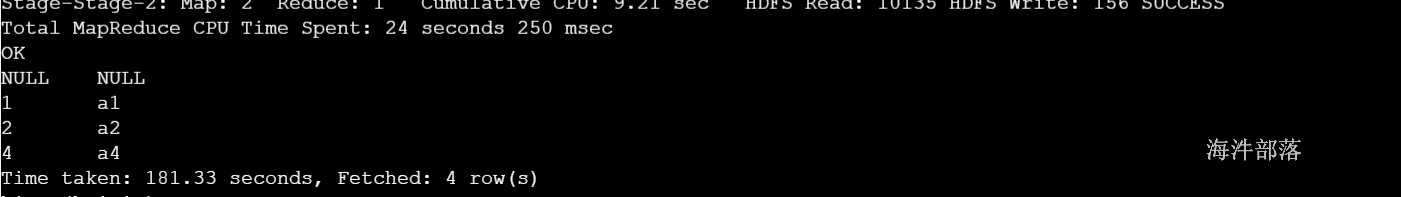
select a.id,a.name,b.id,b.name from test_a a left join test_b b on a.id=b.id
union
select a.id,a.name,b.id,b.name from test_a a right join test_b b on a.id=b.id;为什么呢?
解决方案:
当带有union 的时候, 多个结果集join,需要把字段写清楚,否则union 的时候,得到的数据超乎你的想象。
select a.id as aid, a.name as aname, b.id as bid, b.name as bname from test_a a left join test_b b on a.id = b.id
union
select a.id as aid, a.name as aname, b.id as bid, b.name as bname from test_a a right join test_b b on a.id = b.id;结果:
NULL NULL 3 b3
1 a1 1 b1
2 a2 NULL NULL
4 a4 4 b4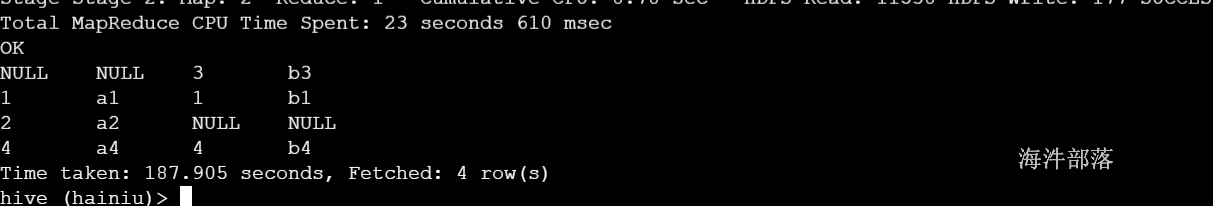
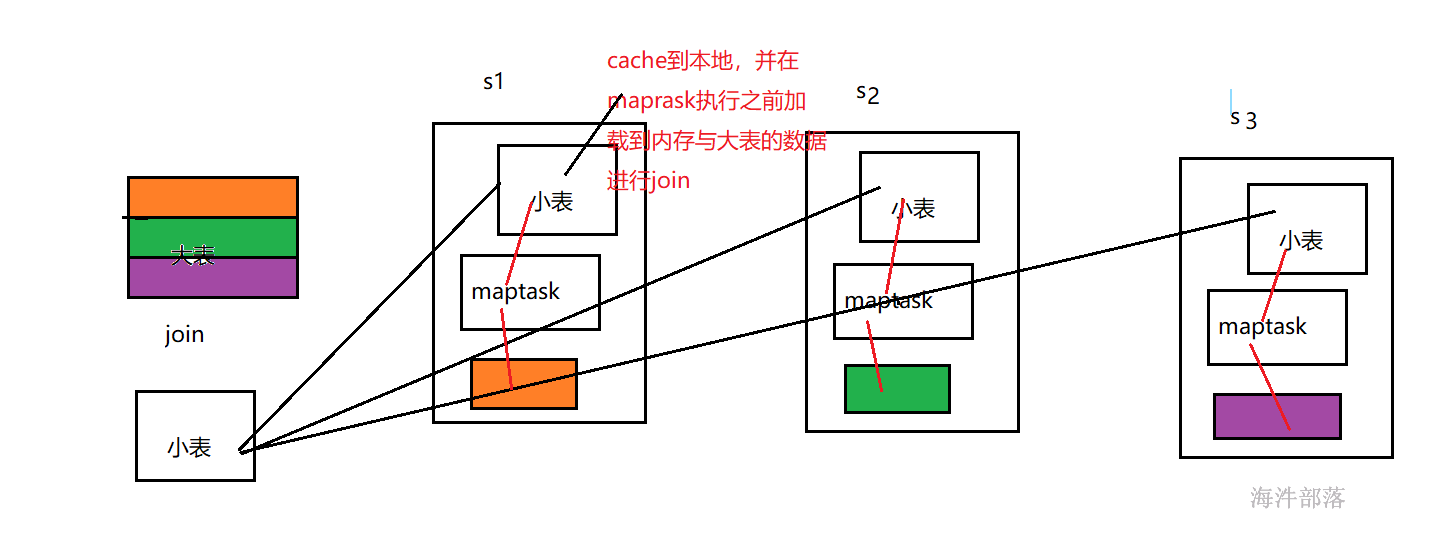
2.6 map端的join
制作字典文件country_dict.dat
http://www.jctrans.com/tool/gjym.htm
--创建表
create table country_dict(
code string,
name string,
region string
)ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t';
--加载数据
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/country.dict' OVERWRITE INTO TABLE country_dict;
类似于mapreduce的mapjoin,在map端join,无reduce。
小表放内存,与大表的数据在map端进行join。
-- 将小表刷入内存中,默认是true
set hive.auto.convert.join=true;
set hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint=true;
-- 刷入内存表的大小(字节),根据自己的数据集加大
set hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize=2500000;
--设置太大也不会校验,所以要根据实际情况来设置
set hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize=2500000000000000;
--大表join 小表
select * from hainiu.user_install_status_other u
inner join country_dict c
on u.country=c.code
where u.dt='20141228'
limit 10;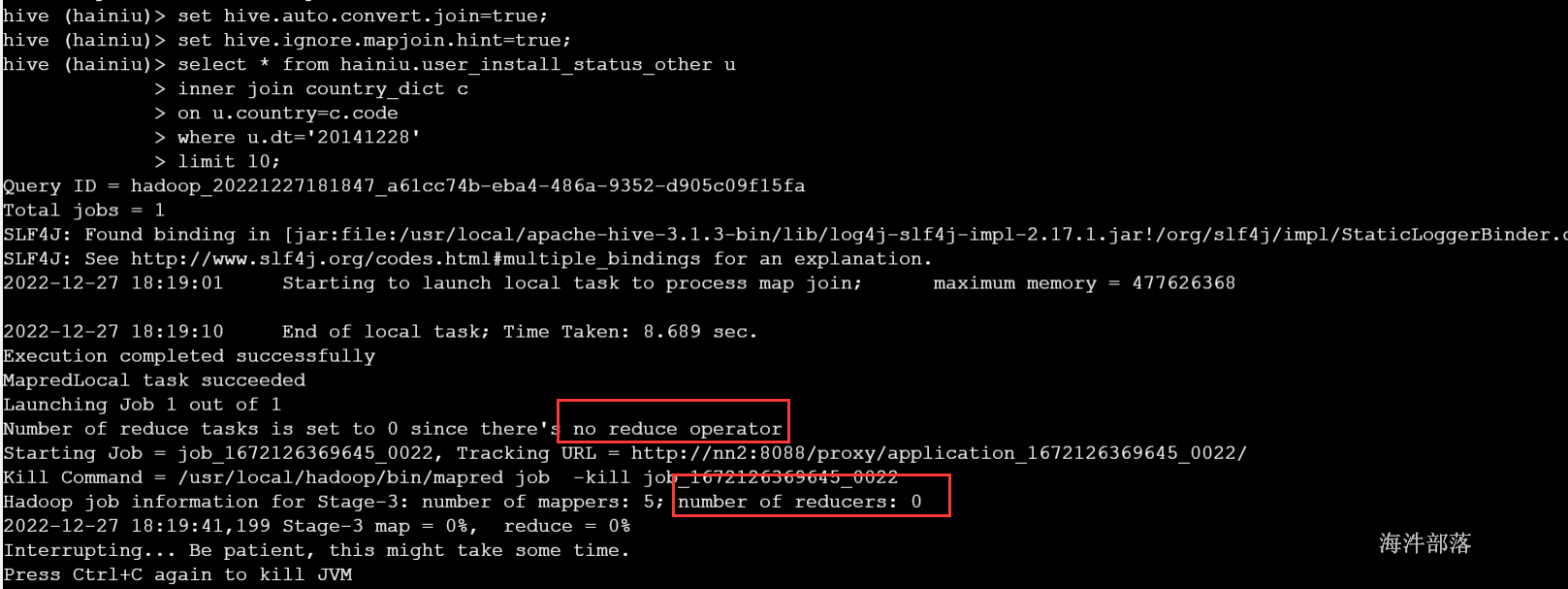
不开启mapjoin 设置:
set hive.auto.convert.join=false;
set hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint=false;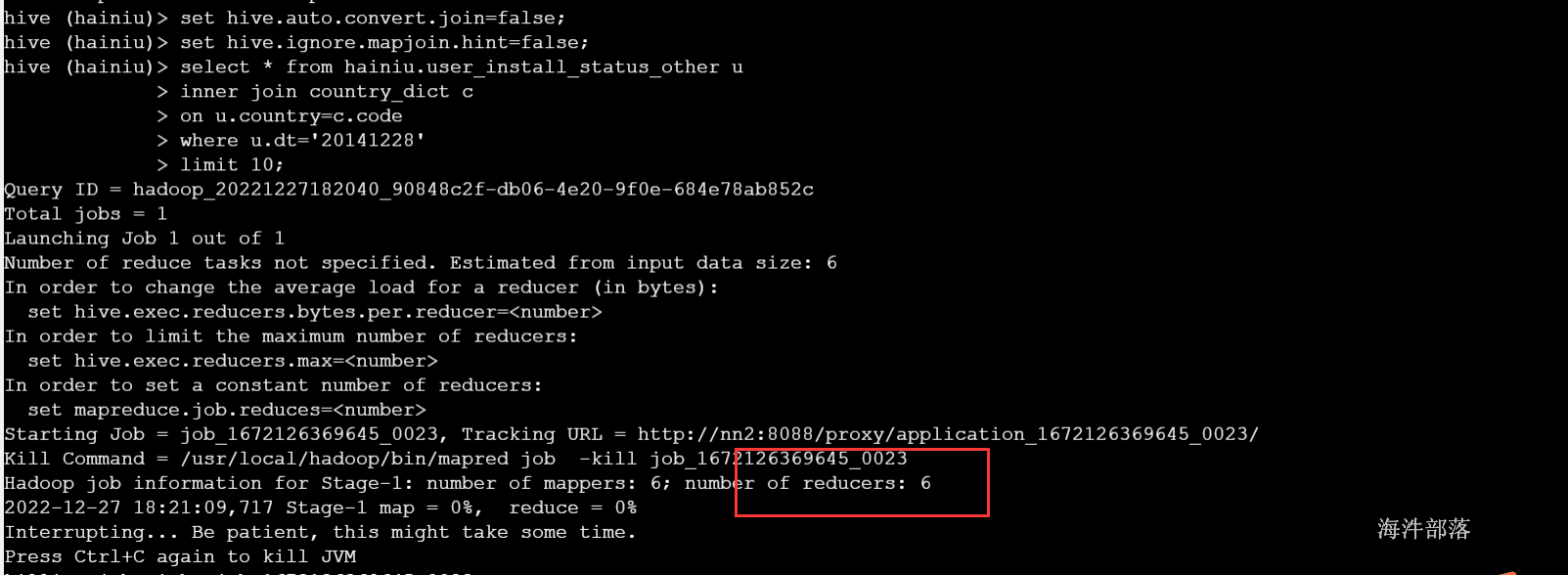
3 GROUP BY
已知student_grouping表
--创建student_grouping表
CREATE TABLE student_grouping(
id int,
name string,
age int,
sex string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t';
--给表导入数据
1 name1 12 boy
2 name2 12 boy
3 name3 13 girl
4 name4 13 boy
5 name5 14 boy
6 name6 14 boy
7 name7 15 girl
8 name8 15 girl
写统计SQL
1)查询总记录数;
2)按照年龄分组,统计记录数;
3)按照性别分组,统计记录数;
4)按照年龄、性别分组,统计记录数;
--写统计SQL
--1)查询总记录数;
select count(*) from student_grouping;
--2)按照年龄分组,统计记录数;
select age, count(*) from student_grouping group by age;
--3)按照性别分组,统计记录数;
select sex, count(*) from student_grouping group by sex;
--4)按照年龄、性别分组,统计记录数;
select age, sex, count(*) from student_grouping group by age, sex;
-- 需求, 一个SQL查询出上面4种查询结果
--在同一个sql中的不同的job是否可以同时运行,默认为false
set hive.exec.parallel=true;
--增加同一个sql允许并行任务的最大线程数
select null as age, null as sex, count(*) as num from student_grouping
union
select age, null as sex, count(*) as num from student_grouping group by age
union
select null as age, sex, count(*) as num from student_grouping group by sex
union
select age, sex, count(*) as num from student_grouping group by age, sex;
NULL NULL 8
NULL boy 5
NULL girl 3
12 NULL 2
12 boy 2
13 NULL 2
13 boy 1
13 girl 1
14 NULL 2
14 boy 2
15 NULL 2
15 girl 2
-- 用 grouping sets 优化后的
select age, sex, count(*) as num from student_grouping group by age, sex
grouping sets((),age, sex, (age, sex));
NULL NULL 8
NULL boy 5
NULL girl 3
12 NULL 2
12 boy 2
13 NULL 2
13 boy 1
13 girl 1
14 NULL 2
14 boy 2
15 NULL 2
15 girl 2
-- 将查询的多个维度的数据导入到hive表里(模拟MySQL)
create table student_count as
select age, sex, count(*) as num from student_grouping group by age, sex
grouping sets((),age, sex, (age, sex));
-- 模拟MySQL出指标
-- 统计总记录数;
select * from student_count where age is null and sex is null;
--统计每个年龄记录数;
select * from student_count where age is not null and sex is null;
--统计性别记录数;
select * from student_count where age is null and sex is not null;
--统计年龄、性别组合的记录数;
select * from student_count where age is not null and sex is not null;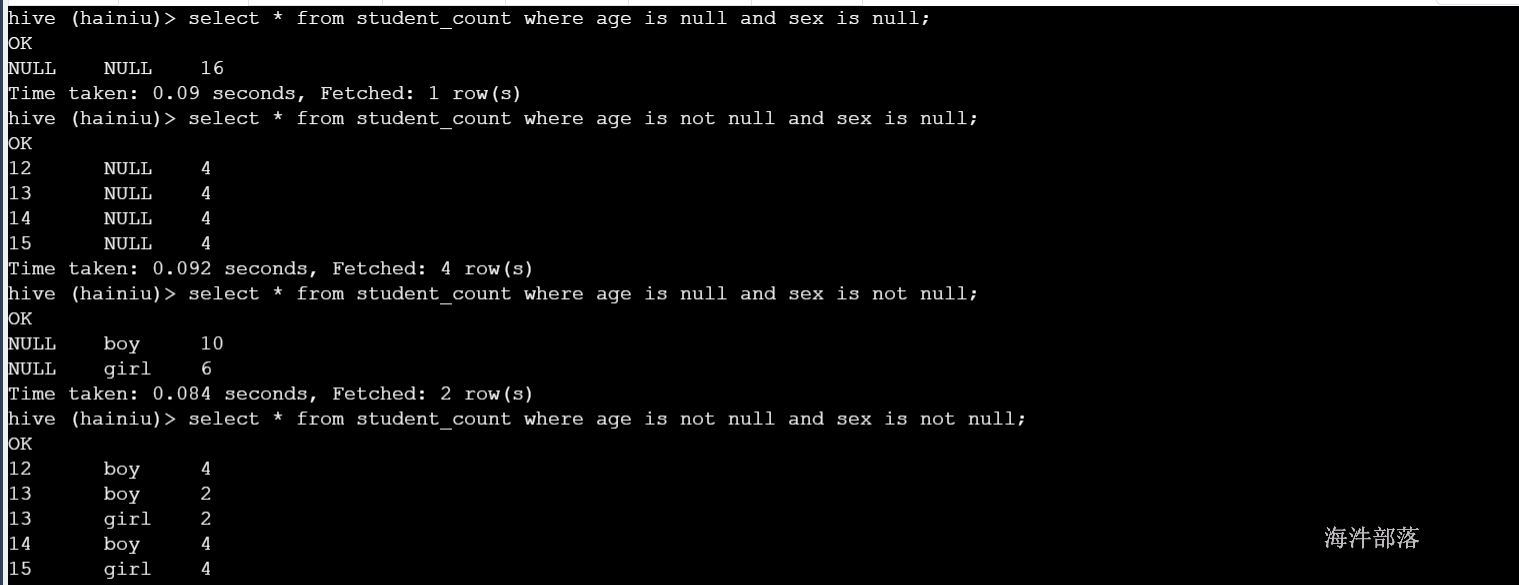
3.1 GROUPING SETS使用
grouping sets是一种将多个group by 逻辑写在一个sql语句中的便利写法。
--GROUP BY a, b GROUPING SETS ((a,b))
SELECT a, b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a, b GROUPING SETS ((a,b))
等于
SELECT a, b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a, b
--GROUP BY a, b GROUPING SETS ((a,b), a)
SELECT a, b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a, b GROUPING SETS ((a,b), a)
等于
SELECT a, b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a, b
UNION ALL
SELECT a, null, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a
--GROUP BY a, b GROUPING SETS (a,b)
SELECT a,b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a, b GROUPING SETS (a,b)
等于
SELECT a, null, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a
UNION ALL
SELECT null, b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY b
--GROUP BY a, b GROUPING SETS ((a, b), a, b, ())
SELECT a, b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a, b GROUPING SETS ((a, b), a, b, ())
等于
SELECT a, b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a, b
UNION ALL
SELECT a, null, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY a
UNION ALL
SELECT null, b, SUM(c) FROM tab1 GROUP BY b
UNION ALL
SELECT null, null, SUM(c) FROM tab1常用于计算各种组合的报表数据。
给null 赋个默认值
select coalesce(age, 'ALL'), coalesce(sex, 'ALL'), count(*) as num from student_grouping group by age, sex
grouping sets((),age, sex, (age, sex));
ALL ALL 8
ALL boy 5
ALL girl 3
12 ALL 2
12 boy 2
13 ALL 2
13 boy 1
13 girl 1
14 ALL 2
14 boy 2
15 ALL 2
15 girl 23.2 with cube是group by中所有key的组合
select
coalesce(age,'ALL'),
if(sex is null, 'ALL', sex),
count(*)
from student_grouping group by age, sex
grouping sets((), age, sex, (age,sex));
-- 等效
select
coalesce(age,'ALL'),
if(sex is null, 'ALL', sex),
count(*)
from student_grouping group by age, sex with cube;group by a,b,c with cube
等效
group by a,b,c grouping sets((a,b,c), (a,b), (a,c), (b,c), a, b, c, ())
3.3 with rollup是按右侧递减的顺序组合
-- GROUP BY age, sex with rollup 等效于 GROUP BY age, sex GROUPING SETS ( (age,sex),age,() )
-- 相当于按右侧递减的顺序group by
SELECT if(age is not null, age, 'ALL'),
case when sex is not null then sex
else 'ALL'
end as age,
count(id) FROM student_grouping GROUP BY age, sex
with rollup;
--等于
SELECT if(age is not null, age, 'ALL'),
case when sex is not null then sex
else 'ALL'
end as age,
count(id) FROM student_grouping GROUP BY age, sex
GROUPING SETS ( (age,sex),age,() );例如:group by a,b,c with rollup
group by a,b,c grouping sets((a,b,c), (a,b), (a), ())


